| Professional charting tools for .Net developers |
Introducing SharpPlot
Your First Chart
Recent Updates
Tutorials
General Tutorials
Chart Tutorials
Reference
SharpPlot Class
Properties
Methods
Structures
Enumerations
Style examples
Glossaries
Active Charts
VectorMath Class
DBUtil Class
Get SharpPlot
Download SharpPlot
Buying SharpPlot
SharpPlot Support
Upgrading from GraPL
Release notes
Home > Sample Charts > CloudChart > Fitted quadratic surface
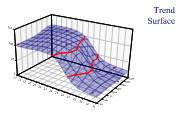
Fitted quadratic surface
The Cloud chart is essentially a scatter-plot in 3 dimensions (maybe you are running an experiment in which you vary pressure and temperature, and are interested in the yield of the result). Rather than fitting a line to show the relationship between input and output, you fit a plane (if the data is linear in both x and y) or a curved surface.
The model in this case is quadratic in the X-direction and linear in Y to give the simple folded surface shown. The order of fit may be up to 4 (quartic) in either direction.
Note that the equation has been used to create a legend for the chart, using a supplied format string.
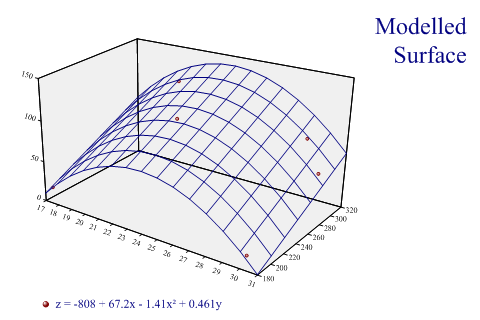
SharpPlot sp = new SharpPlot; sp.SetMargins(24,32,18,6); sp.Heading = "Modelled\nSurface"; sp.HeadingStyle = HeadingStyles.Right; zdata = new int[] {12,65,77,117,9,112}; xdata = new int[] {17,31,29,21,30,24}; ydata = new int[] {190,270,310,300,190,230}; sp.SetZTickMarks(50); sp.CloudChartStyle = CloudChartStyles.WallShading|CloudChartStyles.ModelFit; sp.SetWallFillStyles(FillStyle.Halftone); sp.SetOrderOfFit(2,1); sp.EquationFormat = "z = C0 + C1x + C2x² + C3y"; sp.ZAxisStyle = ZAxisStyles.ForceZero; sp.YAxisStyle = YAxisStyles.FlatText; sp.SetPenWidths(1.2); sp.SetMarkers(Marker.Node); sp.DrawCloudChart(xdata,ydata,zdata); sp.SetKeyText(sp.Equation);
Worked Examples
 |
 |
 |
 |