| Professional charting tools for .Net developers |
Introducing SharpPlot
Your First Chart
Recent Updates
Sample Charts
Tutorials
General Tutorials
Chart Tutorials
SharpPlot Class
Properties
Structures
Enumerations
Style examples
Glossaries
Active Charts
VectorMath Class
DBUtil Class
Get SharpPlot
Download SharpPlot
Buying SharpPlot
SharpPlot Support
Upgrading from GraPL
Release notes
Reference > Methods > DrawCloudChart Method
SharpPlot.DrawCloudChart Method
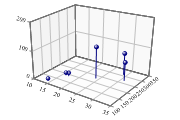
Draw 3D grid and construct 3D Scatter from x,y and z values.
Example
sp.SetMargins(0,12,18,4); sp.SetMarkers(Marker.Bullet); ydata = new int[] {190,270,310,120,190,230}; xdata = new int[] {17,31,29,14,16,24}; zdata = new int[] {12,65,77,7,9,112}; sp.CloudChartStyle = CloudChartStyles.WallShading|CloudChartStyles.GridLines| CloudChartStyles.Risers; sp.SetMarkers(Marker.Ball); sp.SetXTickMarks(5); sp.SetYTickMarks(50); sp.SetZTickMarks(100); sp.Perspective = 6; sp.SetAxisStyle(Color.Gray,LineStyle.Solid,0.5); sp.DrawCloudChart(xdata,ydata,zdata);
The short tutorial shows a few of the possibilities and some sample code.
Overloads
- public void DrawCloudChart(int[] xValues,int[] yValues,int[] zValues);
- public void DrawCloudChart(string[] xCategories,int[] yValues,int[] zValues);
- public void DrawCloudChart(int[] xValues,string[] yCategories,int[] zValues);
- public void DrawCloudChart(double[] xValues,double[] yValues,double[] zValues);
- public void DrawCloudChart(string[] xCategories,int[] yValues,double[] zValues);
- public void DrawCloudChart(int[] xValues,string[] yCategories,double[] zValues);
- public void DrawCloudChart(string[] xCategories,string[] yCategories,int[] zValues);
- public void DrawCloudChart(string[] xCategories,string[] yCategories,double[] zValues);
- public void DrawCloudChart(int[] xValues,int[] yValues,double[][] zValues);
- public void DrawCloudChart(double[] xValues,double[] yValues,double[][] zValues);
Description
The Cloud chart is essentially a scatter-plot in 3 dimensions (maybe you are running an experiment in which you vary pressure and temperature, and are interested in the yield of the result). Rather than fitting a line to show the relationship between input and output, you fit a plane (if the data is linear in both x and y) or a curved surface. The markers are often located in XY-space by drawing risers from the ‘paper’ – this makes it much easier to visualise where they are positioned.
In fact, the Cloudchart is much more versatile than this, as it can also be drawn with lines connecting the points, or planes shaded down to the XY plane (the Z-value is always assumed to be drawn vertically). The Tutorial gives several more examples, and of course multiple charts may be combined using a common set of axes to make quite complex diagrams in 3 dimensions.
See also ...
Scatterplots in 3D | SharpPlot Members | CloudChartStyle Property