| Professional charting tools for .Net developers |
Introducing SharpPlot
Your First Chart
Recent Updates
Tutorials
General Tutorials
Chart Tutorials
Reference
SharpPlot Class
Properties
Methods
Structures
Enumerations
Style examples
Glossaries
Active Charts
VectorMath Class
DBUtil Class
Get SharpPlot
Download SharpPlot
Buying SharpPlot
SharpPlot Support
Upgrading from GraPL
Release notes
Home > Sample Charts > ResponsePlot > Altitude Shading
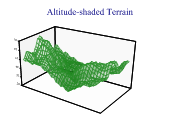
Altitude Shading
This chart is almost always used to illustrate a computed mathematical surface, and could often be combined with a Cloudchart to show a theoretical model overlayed with raw data values.
In the simplest case it takes a rectangular array of arrays of Z-values (effectively a matrix) and treats these as a uniform mesh to be plotted vertically with equally spaced x and y values. An option is to provide either or both of the x and x values as arrays of the correct length, to draw the mesh on a non-uniform scale.
If the mesh genuinely represents ‘altitude’ it can be shaded to represent the range of the Z-axis. This works very well with this style of generated fractal landscape.
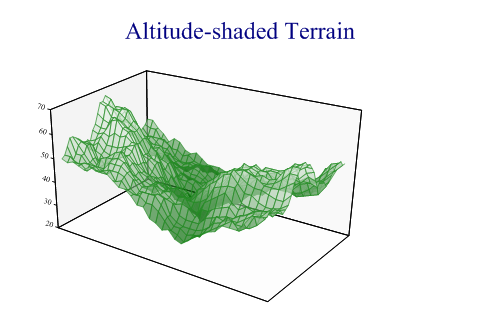
SharpPlot sp = new SharpPlot; sp.SetMargins(48,12,24,0); sp.Heading = "Altitude-shaded Terrain"; sp.ResponsePlotStyle = ResponsePlotStyles.WallShading| ResponsePlotStyles.TiledSurface|ResponsePlotStyles.AltitudeShading; sp.XAxisStyle = XAxisStyles.PlainAxis; sp.YAxisStyle = YAxisStyles.PlainAxis; sp.SetFillStyles(FillStyle.Opacity66); sp.SetColors(Color.ForestGreen); sp.DrawResponsePlot(terrainData);
Worked Examples
 |
 |
 |
 |